ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (AFIB) AND THE LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE
WHAT IS
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (AFIB)?
If you have AFib, irregular electrical impulses in the upper chambers of the heart cause those chambers to fibrillate, or quiver. This results in an irregular and frequently rapid heart rate. This irregular beating can also cause an increased risk for developing blood clots, which can lead to a stroke.1
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (AFIB)
AND THE LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE
The left atrial appendage is a muscular pouch connected to the left atrium of the heart. This appendage is a normal part of the heart and causes no problems in the general population. However, the left atrial appendage can be a major source of blood clots in people with AFib.2
During AFib, blood clots have the potential to form in the left atrial appendage. If the blood clots are pumped out into the body, the clots may flow to the brain and lead to stroke.
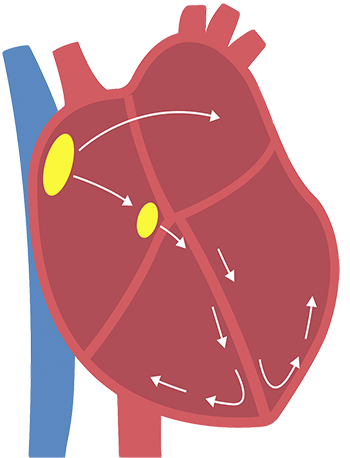
Normal heart
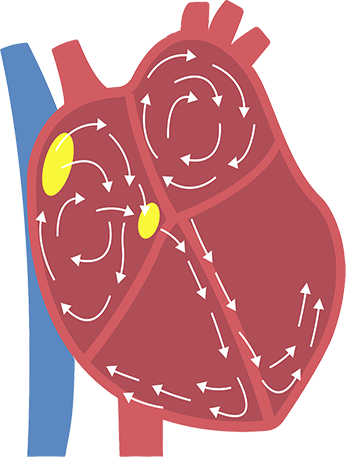
Atrial fibrillation
WHAT ARE THE
SYMPTOMS OF AFIB?1
HEART PALPITATIONS

FAINTING

LIGHTHEADEDNESS
SHORTNESS OF BREATH

CHEST PAIN
WHAT ARE THE
RISK FACTORS FOR AFIB?
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE

VALVULAR HEART DISEASE

HEART
FAILURE
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE

CARDIOMYOPATHY

CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
DIABETES
SMOKING
EXCESSIVE ALCOHOL USE
AFIB TREATMENT
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with Atrial Fibrillation (AFib), it’s important to seek timely treatment since the condition increases the risk for stroke. Your doctor will discuss the best treatment option for you.
MAT-2304810 v3.0 | Item approved for U.S. use only.